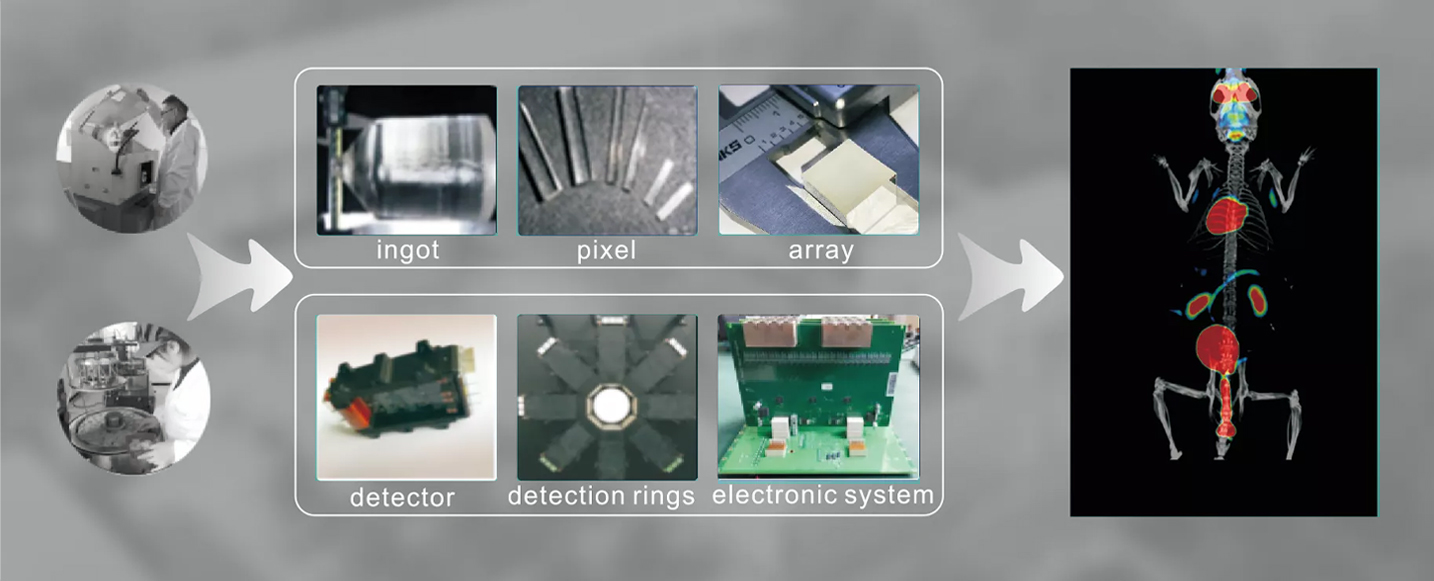
The most commonly used animal model in medicine and pharmacy is the mouse model. Professor Simon R. Cherry's team at UC Davis proposed in a paper published in the top journal JNM that "clear PET imaging of mice requires spatial resolution to achieve
We refer to small animal PET with a spatial resolution of 0.5mm as "microscopic" small animal PET.
pour"A spatial resolution of -0.5 mm is required for a small-animal PET scanner if one wants to image the mousewith the same relative spatial resolution as achieved in a human using a clinical whole body PET scanner with 5mm spatialresolution(5,6)”.[Literature sources: JNucl Med.2016 July;57(7): 1130-1135.]
Medyinghua's small animal PET uses independently developed submillimeter PET probes with a spatial resolution of 0.42mm, ushering in the era of clear PET images of mice.
The most commonly used animal model in medicine and pharmacy is the mouse model. Professor Simon R. Cherry's team at UC Davis proposed in a paper published in the top journal JNM that "clear PET imaging of mice requires spatial resolution to achieve
We refer to small animal PET with a spatial resolution of 0.5mm as "microscopic" small animal PET.
pour"A spatial resolution of -0.5 mm is required for a small-animal PET scanner if one wants to image the mousewith the same relative spatial resolution as achieved in a human using a clinical whole body PET scanner with 5mm spatialresolution(5,6)”.[Literature sources: JNucl Med.2016 July;57(7): 1130-1135.]
Medyinghua's small animal PET uses independently developed submillimeter PET probes with a spatial resolution of 0.42mm, ushering in the era of clear PET images of mice.
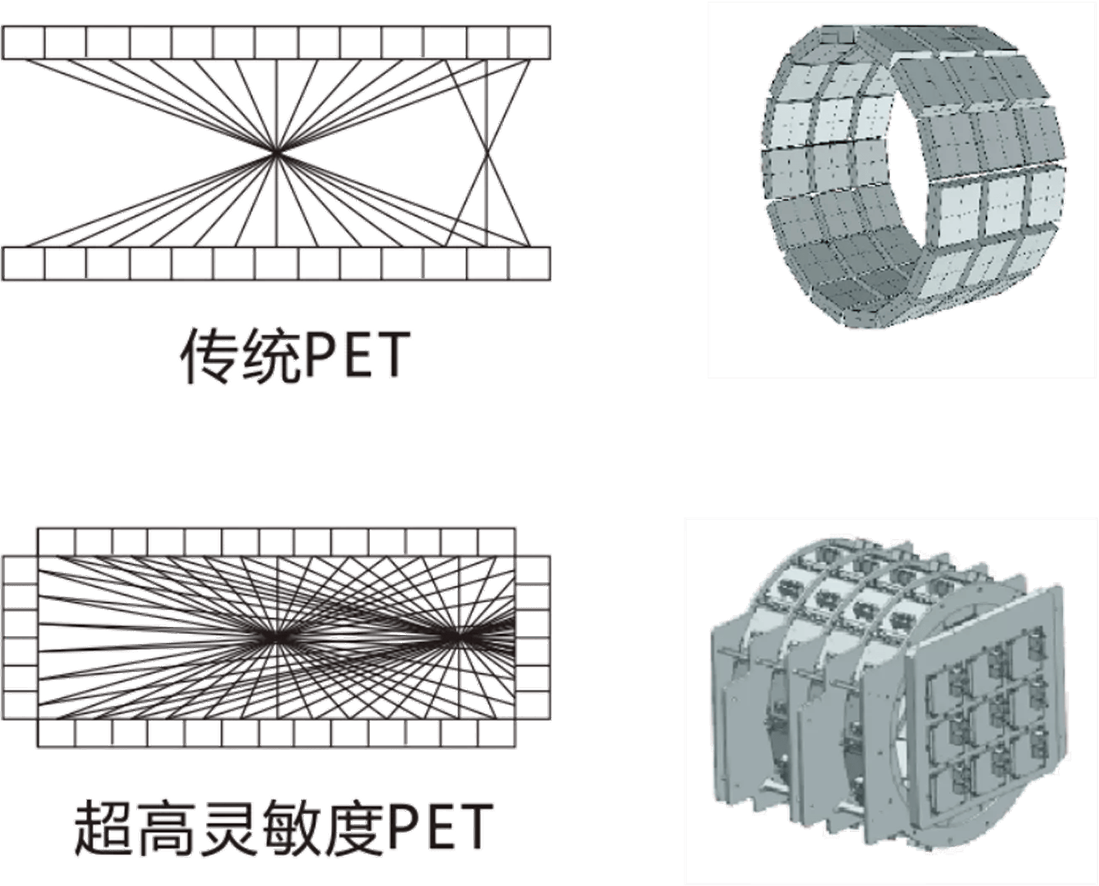
Positron emission tomography (PET) has an unparalleled role in detecting metabolic function in live animals, as it has extremely high sensitivity and almost unit cell level perception ability compared to other imaging methods. It not only plays a significant role in many disciplines such as oncology, neuroscience, cardiology, genetics, radiology, immunology, genomics, but also serves as a powerful tool for various new drug development and research. Especially for primate experimental animals, due to their closer relationship with humans, small animals (mainly mice) play an irreplaceable role in the early stages of drug screening, pharmacology, efficacy testing, and mid-term drug safety evaluation in the process of new drug development. However, traditional PET uses circular detectors (axial field of view 9-50cm) with low sensitivity and uneven imaging time of 1-30 minutes, which severely limits their scanning speed. Only local dynamic imaging can be tracked, such as the brain and heart, while the study of drug metabolism dynamics in large animals requires whole-body dynamic imaging, which existing equipment cannot meet the requirements.
Medyinghua is the world's first to propose "ultra-high sensitivity PET technology", upgrading traditional circular detectors to 4 π solid angle detection, increasing PET scanning time from minutes to sub seconds, and achieving sub second PET imaging. Ultra high sensitivity PET will bring new imaging tools to the research and development of pharmacology, pathology, physiology, and other biomedical fields, and its promoting effect on the research and development of biomedical fields is immeasurable.
Positron emission tomography (PET) has an unparalleled role in detecting metabolic function in live animals, as it has extremely high sensitivity and almost unit cell level perception ability compared to other imaging methods. It not only plays a significant role in many disciplines such as oncology, neuroscience, cardiology, genetics, radiology, immunology, genomics, but also serves as a powerful tool for various new drug development and research. Especially for primate experimental animals, due to their closer relationship with humans, small animals (mainly mice) play an irreplaceable role in the early stages of drug screening, pharmacology, efficacy testing, and mid-term drug safety evaluation in the process of new drug development. However, traditional PET uses circular detectors (axial field of view 9-50cm) with low sensitivity and uneven imaging time of 1-30 minutes, which severely limits their scanning speed. Only local dynamic imaging can be tracked, such as the brain and heart, while the study of drug metabolism dynamics in large animals requires whole-body dynamic imaging, which existing equipment cannot meet the requirements.
Medyinghua is the world's first to propose "ultra-high sensitivity PET technology", upgrading traditional circular detectors to 4 π solid angle detection, increasing PET scanning time from minutes to sub seconds, and achieving sub second PET imaging. Ultra high sensitivity PET will bring new imaging tools to the research and development of pharmacology, pathology, physiology, and other biomedical fields, and its promoting effect on the research and development of biomedical fields is immeasurable.