Selected Client Papers | 18F-FAPI PET/CT visualization of fibrotic remodeling in pulmonary hypertension: a Madic high-resolution imaging-based study
Release Date:2025-05-28 Number of views:329
The research result of the team of Department of Nuclear Medicine and Department of Respiratory Medicine of the First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou Medical University, "Targeting Fibroblast Activation Protein for Molecular Imaging of Fibrotic Remodeling in Pulmonary Arterial Targeting Fibroblast Activation Protein for Molecular Imaging of Fibrotic Remodeling in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension" was published in The Journal of Nuclear Medicine (IF: 9.1, the leading journal in the field of nuclear medicine).The MadicLab PSA071 PET/CT scanner provided the following results in the study 18F-FAPI PET/CT images of live rats and quantitative analysis results.
Research Background and Innovative Breakthroughs
Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) is a highly lethal cardiovascular disease with pulmonary artery remodeling and right ventricular fibrosis as core pathologic features. Conventional tissue biopsy is difficult to achieve early fibrosis dynamic monitoring due to invasiveness and sampling limitations. In this study, the first non-invasive visual assessment of fibrotic remodeling in PAH was achieved using 18F-labeled fibroblast activation protein inhibitor (FAPI) PET/CT technology in combination with the MadicLab PSA071 high-resolution imaging system (spatial resolution <0.5 mm).
Core research content
Animal model validation: spatial and temporal correlation of early fibrosis
• Model construction: A rat model of PAH was induced by wild lily base (MCT), and 18F-FAPI uptake was dynamically tracked by MadicLab PET/CT on days 7, 14, and 21 post-injection.
• Key Findings:
18F-FAPI uptake peaked in myocardium and lung tissue on day 14 (SUVr myocardium 2.13±0.76), which preceded the increase in right ventricular systolic blood pressure (which was significantly elevated on day 14) and the exacerbation of collagen deposition (which peaked on day 21).
Immunofluorescence confirmed co-localization of FAPI uptake with activated fibroblast markers (waveform proteins), validating the pathologic specificity of the imaged signal.
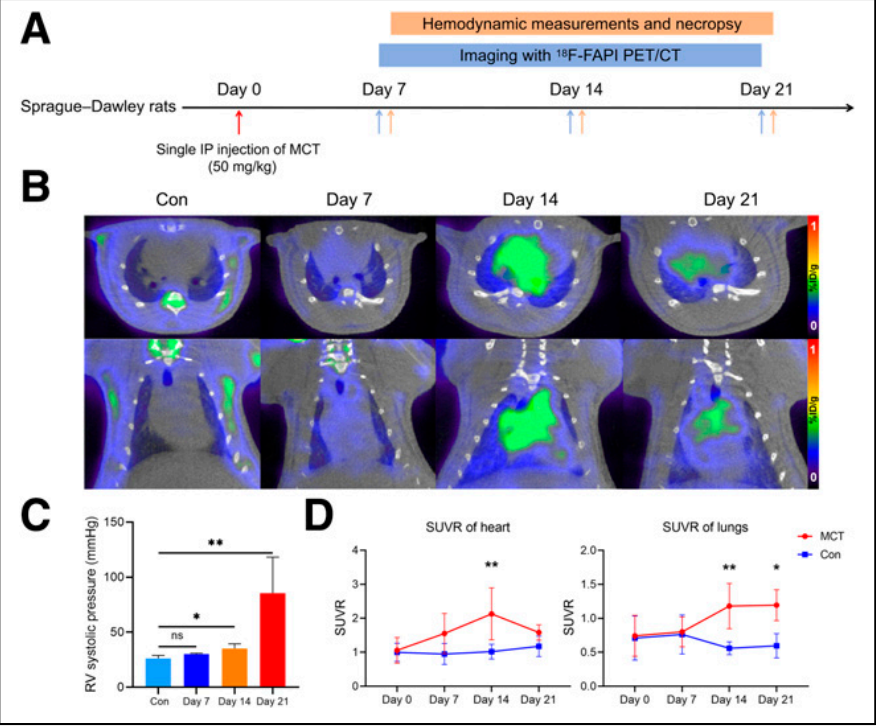
Figure 1: Time course of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) progression and 18F-FAPI uptake in myocardial and lung tissues of MCT rats. (A) Schematic of animal experiments. (B) Serial serial serial 18F-FAPI PET/CT images (transverse and coronal) of the MCT-induced PAH model. (C) Right ventricular systolic blood pressure gradually increased with the progression of PAH, showing a significant difference from day 14 onward (using the Kruskal-Wallis test). (D) Changes in 18F-FAPI uptake in MCT rats at different time points (two-way ANOVA was used between MCT and control groups). Control (Con) Day 7 and 14: n=5; Day 21: n=3 (A-D). *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ns=no significant difference. ip=peritoneal injection; SUVR=standardized uptake value ratio.
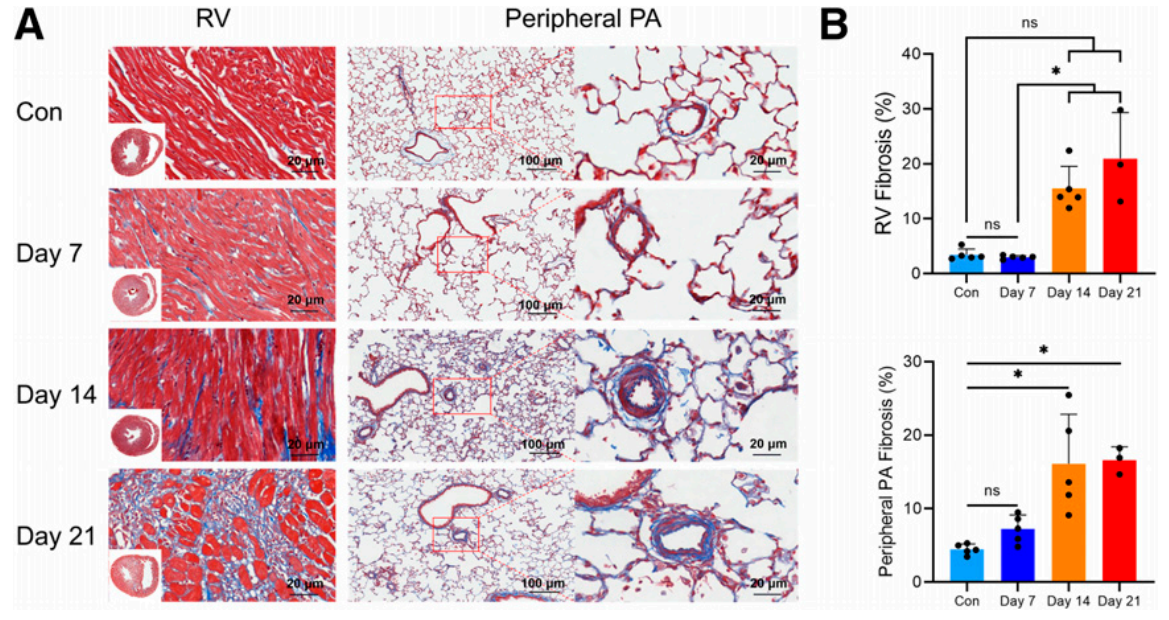
Figure 2.: Fibrosis patterns in the right ventricle (RV) and peripheral pulmonary artery (PA) of the lungs of MCT rats. (A) Representative images of Masson trichrome-stained right ventricle and lung tissue sections (collagen in blue) at corresponding time intervals. Scale bars are 20 μm and 100 μm, respectively. (B) Planar quantitative analysis of fibrosis (Masson trichrome-stained blue areas as a percentage of the total tissue surface area) showed a gradual increase in fibrosis in the right ventricle and peripheral pulmonary arteries of the lungs of MCT rats. The Kruskal-Wallis test was used. Control (Con) day 7 and 14: n=5; day 21: n=3 (A and B). *P<0.05, ns=not significantly different.
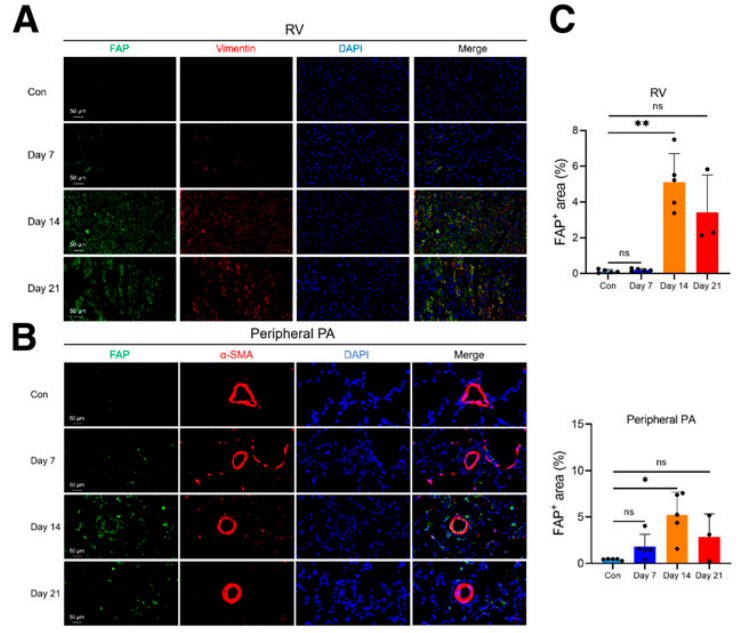
Figure 3: Immunofluorescence staining of fibroblast activation protein (FAP) in the right ventricle (RV) and peripheral pulmonary artery (PA) of the lungs of MCT rats. (A) Representative images of FAP immunofluorescence staining of right ventricular sections at corresponding time intervals (FAP, green; waveform protein, red; 4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole [DAPI], blue). Scale bar is 50 μm. (B) Representative images of FAP immunofluorescence staining of lung tissue sections at corresponding time intervals (FAP, green; α-smooth muscle actin [α-SMA], red; DAPI, blue). Scale bar is 50 μm. (C) FAP expression in the right ventricle and peripheral pulmonary arteries peaked on day 14 and began to decline on day 21. Control (Con) Day 7 and 14: n=5; day 21: n=3. *P<0.05 (Kruskal-Wallis test); ns=not significantly different.
2. Clinical studies: quantitative association of fibrotic load with condition
· Enrollment Cohort: 38 patients with PAH (mean age 34±11 years, 65.8% female), 97.4% had detectable abnormal 18F-FAPI uptake in the right heart and pulmonary artery.
· Functional correlations: The intensity of
uptake (SUVmax) was positively correlated with pulmonary artery pressure (mPAP 57.2±16.9 mmHg), WHO functional class, and negatively correlated with right ventricular function indices.
In 3 of 5 follow-up patients, uptake was reduced and clinical symptoms improved after PAH-targeted therapy, suggesting the potential of imaging to monitor response to therapy.
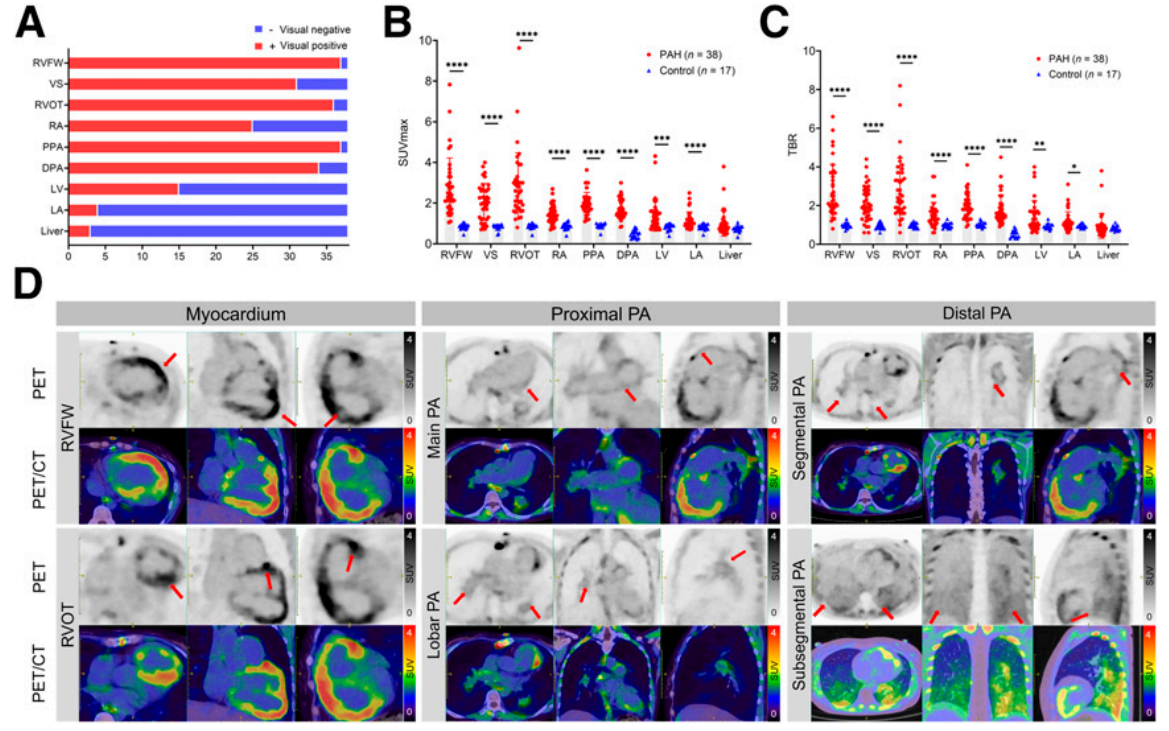
FIGURE 4. Visual qualitative assessment and semiquantitative analysis of chest PET/CT images
(A) Visual assessment findings in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH). The right ventricular free wall (RVFW) and proximal pulmonary artery (PPA) had the highest rate of positive 18F-FAPI uptake (37/38, 97%). In addition to the right side of the heart and pulmonary arteries, 18F-FAPI uptake was also observed in the left ventricle (LV), left atrium (LA), and liver.
(B and C) Maximum standardized uptake values (SUVmax) and target-to-benefit ratios (TBR) were significantly higher in the myocardium and pulmonary arteries of PAH patients than in the control group. Differences between groups were calculated using the Mann-Whitney U test.
(D) Representative 18F-FAPI PET/CT images of PAH patients:
Device Application Highlights
The MadicLab PSA071 PET/CT System played a key role in the study:
· High-resolution imaging: accurately captures early fibrosis signals in the pulmonary artery wall (as thin as 0.5 mm) and myocardium.
· Quantitative capabilities: Quantifying the fibrotic load through SUV ratios and target-to-background ratios (TBRs), providing data to support pathologic correlation.
Significance and Prospects
This study demonstrates for the first time that 18F-FAPI PET/CT combined with MadicLab high-resolution imaging can noninvasively assess the progression of PAH fibrosis, providing a new tool for early diagnosis and therapeutic monitoring. Although a larger sample is needed to validate the prognostic value, its advantages in avoiding biopsy trauma and dynamically tracking the therapeutic efficacy are expected to promote the development of PAH diagnosis in the direction of precision and non-invasive treatment.
Link to paper: DOI: 10.2967/jnumed.124.268376
Equipment Support: MadicLab PSA071 PET/CT System (Shandong Madec Yinghua Technology Co., Ltd.)
The research result of the team of Department of Nuclear Medicine and Department of Respiratory Medicine of the First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou Medical University, "Targeting Fibroblast Activation Protein for Molecular Imaging of Fibrotic Remodeling in Pulmonary Arterial Targeting Fibroblast Activation Protein for Molecular Imaging of Fibrotic Remodeling in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension" was published in The Journal of Nuclear Medicine (IF: 9.1, the leading journal in the field of nuclear medicine).The MadicLab PSA071 PET/CT scanner provided the following results in the study 18F-FAPI PET/CT images of live rats and quantitative analysis results.

Research Background and Innovative Breakthroughs
Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) is a highly lethal cardiovascular disease with pulmonary artery remodeling and right ventricular fibrosis as core pathologic features. Conventional tissue biopsy is difficult to achieve early fibrosis dynamic monitoring due to invasiveness and sampling limitations. In this study, the first non-invasive visual assessment of fibrotic remodeling in PAH was achieved using 18F-labeled fibroblast activation protein inhibitor (FAPI) PET/CT technology in combination with the MadicLab PSA071 high-resolution imaging system (spatial resolution <0.5 mm).
Core research content
Animal model validation: spatial and temporal correlation of early fibrosis
• Model construction: A rat model of PAH was induced by wild lily base (MCT), and 18F-FAPI uptake was dynamically tracked by MadicLab PET/CT on days 7, 14, and 21 post-injection.
• Key Findings:
18F-FAPI uptake peaked in myocardium and lung tissue on day 14 (SUVr myocardium 2.13±0.76), which preceded the increase in right ventricular systolic blood pressure (which was significantly elevated on day 14) and the exacerbation of collagen deposition (which peaked on day 21).
Immunofluorescence confirmed co-localization of FAPI uptake with activated fibroblast markers (waveform proteins), validating the pathologic specificity of the imaged signal.

Figure 1: Time course of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) progression and 18F-FAPI uptake in myocardial and lung tissues of MCT rats. (A) Schematic of animal experiments. (B) Serial serial serial 18F-FAPI PET/CT images (transverse and coronal) of the MCT-induced PAH model. (C) Right ventricular systolic blood pressure gradually increased with the progression of PAH, showing a significant difference from day 14 onward (using the Kruskal-Wallis test). (D) Changes in 18F-FAPI uptake in MCT rats at different time points (two-way ANOVA was used between MCT and control groups). Control (Con) Day 7 and 14: n=5; Day 21: n=3 (A-D). *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ns=no significant difference. ip=peritoneal injection; SUVR=standardized uptake value ratio.

Figure 2.: Fibrosis patterns in the right ventricle (RV) and peripheral pulmonary artery (PA) of the lungs of MCT rats. (A) Representative images of Masson trichrome-stained right ventricle and lung tissue sections (collagen in blue) at corresponding time intervals. Scale bars are 20 μm and 100 μm, respectively. (B) Planar quantitative analysis of fibrosis (Masson trichrome-stained blue areas as a percentage of the total tissue surface area) showed a gradual increase in fibrosis in the right ventricle and peripheral pulmonary arteries of the lungs of MCT rats. The Kruskal-Wallis test was used. Control (Con) day 7 and 14: n=5; day 21: n=3 (A and B). *P<0.05, ns=not significantly different.

Figure 3: Immunofluorescence staining of fibroblast activation protein (FAP) in the right ventricle (RV) and peripheral pulmonary artery (PA) of the lungs of MCT rats. (A) Representative images of FAP immunofluorescence staining of right ventricular sections at corresponding time intervals (FAP, green; waveform protein, red; 4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole [DAPI], blue). Scale bar is 50 μm. (B) Representative images of FAP immunofluorescence staining of lung tissue sections at corresponding time intervals (FAP, green; α-smooth muscle actin [α-SMA], red; DAPI, blue). Scale bar is 50 μm. (C) FAP expression in the right ventricle and peripheral pulmonary arteries peaked on day 14 and began to decline on day 21. Control (Con) Day 7 and 14: n=5; day 21: n=3. *P<0.05 (Kruskal-Wallis test); ns=not significantly different.
2. Clinical studies: quantitative association of fibrotic load with condition
· Enrollment Cohort: 38 patients with PAH (mean age 34±11 years, 65.8% female), 97.4% had detectable abnormal 18F-FAPI uptake in the right heart and pulmonary artery.
· Functional correlations: The intensity of
uptake (SUVmax) was positively correlated with pulmonary artery pressure (mPAP 57.2±16.9 mmHg), WHO functional class, and negatively correlated with right ventricular function indices.
In 3 of 5 follow-up patients, uptake was reduced and clinical symptoms improved after PAH-targeted therapy, suggesting the potential of imaging to monitor response to therapy.

FIGURE 4. Visual qualitative assessment and semiquantitative analysis of chest PET/CT images
(A) Visual assessment findings in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH). The right ventricular free wall (RVFW) and proximal pulmonary artery (PPA) had the highest rate of positive 18F-FAPI uptake (37/38, 97%). In addition to the right side of the heart and pulmonary arteries, 18F-FAPI uptake was also observed in the left ventricle (LV), left atrium (LA), and liver.
(B and C) Maximum standardized uptake values (SUVmax) and target-to-benefit ratios (TBR) were significantly higher in the myocardium and pulmonary arteries of PAH patients than in the control group. Differences between groups were calculated using the Mann-Whitney U test.
(D) Representative 18F-FAPI PET/CT images of PAH patients:
Device Application Highlights
The MadicLab PSA071 PET/CT System played a key role in the study:
· High-resolution imaging: accurately captures early fibrosis signals in the pulmonary artery wall (as thin as 0.5 mm) and myocardium.
· Quantitative capabilities: Quantifying the fibrotic load through SUV ratios and target-to-background ratios (TBRs), providing data to support pathologic correlation.
Significance and Prospects
This study demonstrates for the first time that 18F-FAPI PET/CT combined with MadicLab high-resolution imaging can noninvasively assess the progression of PAH fibrosis, providing a new tool for early diagnosis and therapeutic monitoring. Although a larger sample is needed to validate the prognostic value, its advantages in avoiding biopsy trauma and dynamically tracking the therapeutic efficacy are expected to promote the development of PAH diagnosis in the direction of precision and non-invasive treatment.
Link to paper: DOI: 10.2967/jnumed.124.268376
Equipment Support: MadicLab PSA071 PET/CT System (Shandong Madec Yinghua Technology Co., Ltd.)